Blood Pressure Chart: What Your Readings Say About Your Health
Normal, low, or high – understanding your blood pressure readings are critical for overall health and well-being.
Do you know what the numbers mean when your doctor tells you your blood pressure is 120 over 80? Does it mean it is normal, or is it too high or too low?
Understanding your blood pressure readings is vital for maintaining good health, which is why your healthcare practitioner checks it every time you visit.
This article will help you make sense of your blood pressure numbers by explaining the blood pressure chart.
What Do the Blood Pressure Numbers Mean?
Blood pressure forms when your heart contracts and the blood that is forced through the arteries place pressure on the walls of your blood vessels.
The pressure is necessary to keep your blood flowing so that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the cells throughout the body and waste products are removed.
Your blood pressure readings are made up of 2 numbers. The higher number is called systolic blood pressure and represents the pressure in your arteries when your heart contracts. The lower number is your diastolic blood pressure. It’s the pressure in your arteries between heartbeats when your heart is at rest.
Your systolic and diastolic blood pressure numbers are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) using a mercury, aneroid, or digital blood pressure monitor (also called a sphygmomanometer).
An inflatable cuff is placed around your upper arm and inflated to squeeze the artery in your arm shut. The pressure is then slowly released.
The moment blood starts flowing through the artery again is your diastolic pressure, and when the flow can no longer be detected, it is your systolic pressure, giving you a blood pressure reading of 120 over 80, for example.
Your blood pressure reading varies according to the time of day and what you are doing. For example, it may spike when you’re stressed, but it doesn’t mean you have high blood pressure.
Therefore, to determine whether you have normal, high, or low blood pressure, you should measure it at the same time of day, preferably first thing in the morning and again in the evening for a few consecutive days.
The Blood Pressure Chart
The American Heart Association developed the blood pressure chart below to categorize blood pressure readings. It lists the blood pressure ranges for each of the blood pressure categories, helping you and your doctor determine whether your levels are normal.
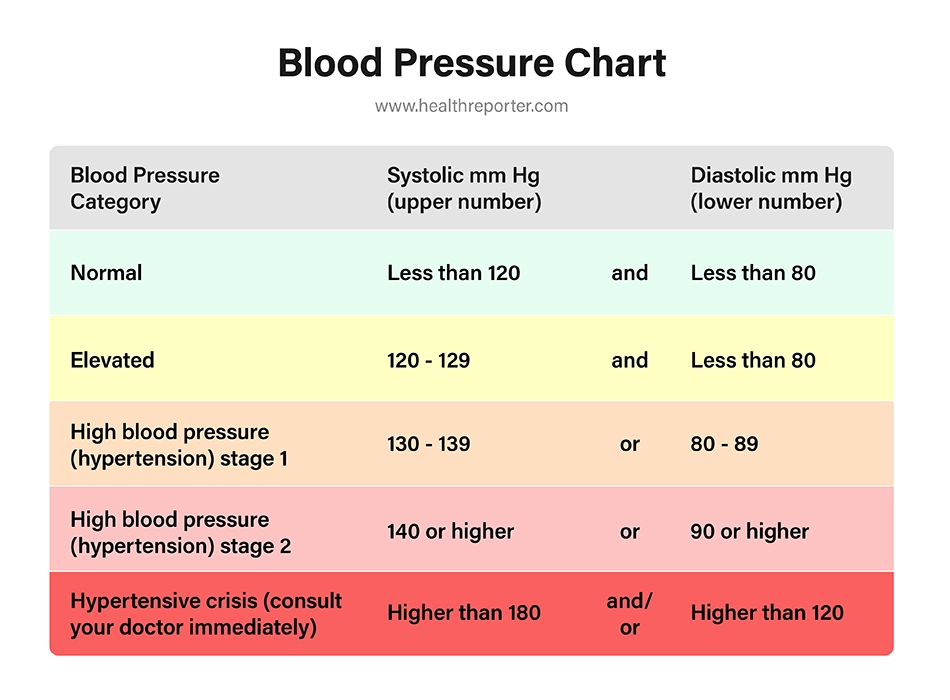
Blood pressure categories
While understanding the variations in blood pressure and identifying the particular categories are essential, it’s also useful to know what the particular numbers mean and how to approach them:
- Normal blood pressure – a blood pressure reading of less than 120 over 80mmHg is considered normal. Follow a heart-healthy diet and exercise regimen to maintain it.
- Elevated blood pressure – your systolic blood pressure is between 120mmHg and 129 mmHg, and your diastolic blood pressure is less than 80mmHg. You should start following medical advice to avoid developing high blood pressure.
- Hypertension: Stage 1 – your systolic blood pressure is consistently between 130 and 139mmHg or your diastolic blood pressure measures between 80 and 89mmHg. You will likely have to introduce considerate lifestyle changes and take blood pressure medication.
- Hypertension: Stage 2 – systolic blood pressure is consistently higher than 140mmHg, and diastolic blood pressure is consistently higher than 90mmHg. Like before, you will be prescribed lifestyle changes and respective medication.
- Hypertensive crisis – a medical emergency. If several consecutive blood pressure readings show systolic pressure and diastolic pressure over 180mmHg and 120mmHg, respectively, you should contact your doctor immediately. Call an ambulance if you experience other symptoms, such as chest or back pain, shortness of breath, or weakness.
The above guidelines were introduced in 2017. Before that, systolic blood pressure of 120-139mmHg was considered high normal. Now, it’s being treated as high blood pressure that needs to be addressed for nearly half of the U.S. population, according to the 2023 data.
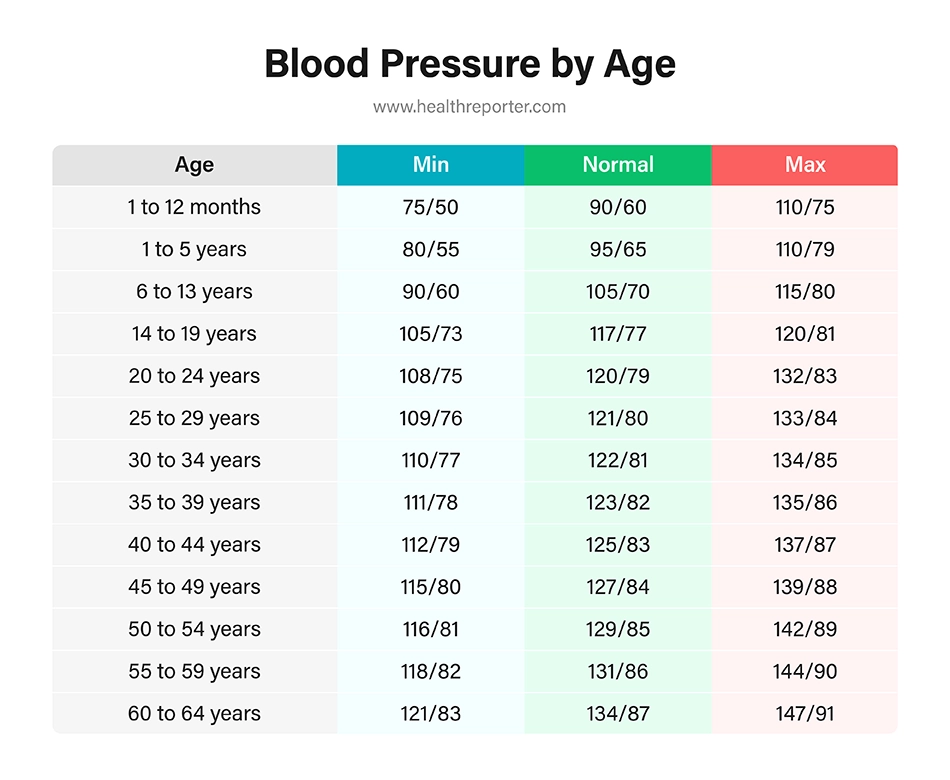
What Is Normal Blood Pressure by Age?
Research shows that blood pressure increases as we age, and normal and high blood pressure levels differ between men and women. The chart below shows healthy blood pressure ranges by age.
What Blood Pressure Is Too Low?
People with low blood pressure have a systolic blood pressure of less than 90mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure of less than 60mmHg. Although low blood pressure may be asymptomatic, it can cause dizziness and fainting.
In extreme cases, low blood pressure may cause loss of consciousness, a weak pulse, shallow, rapid breathing, blurred vision, and clammy skin. These are signs that your low blood pressure is a medical emergency, and you should seek help immediately.
How to Prevent High Blood Pressure?
Many of the risk factors associated with high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease are lifestyle habits. Therefore, some simple lifestyle changes, such as those listed below, can help prevent and manage high blood pressure.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet such as the DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension).
- Maintain a healthy weight. Losing weight if you are overweight can help lower blood pressure.
- Regular exercise helps to reduce stress and strengthens your cardiovascular system.
- Ensure that you get enough good quality sleep. Research shows that people who sleep for less than 6 hours per night have an increased risk of high blood pressure.
- Don’t smoke. Smoking cigarettes causes a spike in blood pressure.
- Limit your intake of alcohol.
- Manage stress and anxiety.
There are also several blood pressure and cardiovascular health apps that can help you keep track of your health and lifestyle choices and improve your blood pressure readings.
A Word from Our MD


Untreated high blood pressure affects all parts of your body. It is a major risk factor for heart disease, heart attack, stroke, hypertensive crisis, sexual dysfunction, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Therefore, the American Heart Association recommends that everyone should be familiar with their blood pressure numbers and regularly have their levels checked.
The blood pressure chart makes it easy for healthcare providers and patients alike to understand the meaning of a blood pressure reading so that the appropriate lifestyle changes and blood pressure medications can be prescribed should you have raised numbers.
It’s important to note that low blood pressure too can be a sign of underlying medical conditions, so if you experience consistently low levels, be sure to seek medical advice, as well.
FAQs
According to the most recent guidelines, ideal blood pressure is less than 120mmHg and 80mmHg.
Adults aged 18 and older should check their blood pressure at least once every two years. If you have high blood pressure, your doctor may advise more frequent readings.
Then, you should measure your blood pressure at the same time every day, usually first thing in the morning before eating and again at night until your blood pressure is controlled.
People with elevated blood pressure, a family history of hypertension, and health conditions such as kidney disease and diabetes may develop high blood pressure. Age, gender, and ethnicity may also predispose you to hypertension.
Men typically have higher blood pressure than women of the same age. The difference could be 6-10mmHg and is mainly associated with higher levels of androgens that may promote cardiovascular-related diseases.
Conclusion
Preventing and managing high blood pressure is critical for health and longevity. Therefore, you must understand the meaning of your blood pressure numbers.
The blood pressure chart clearly defines 5 blood pressure categories, including normal, elevated blood pressure, 2 stages of hypertension, and hypertensive crisis.
When you know the meaning of your blood pressure readings, you can take steps towards making better lifestyle choices and getting the best treatment from your doctor to help you lead a healthier life.

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: 









