Measuring your blood glucose levels is very important. A hemoglobin test can determine a normal range, but what is considered normal for a healthy adult? We explain what the A1c 5.4 result means on your test and 3 ways you can maintain that blood glucose measurement.
Glycated Hemoglobin A1c: 5.4%
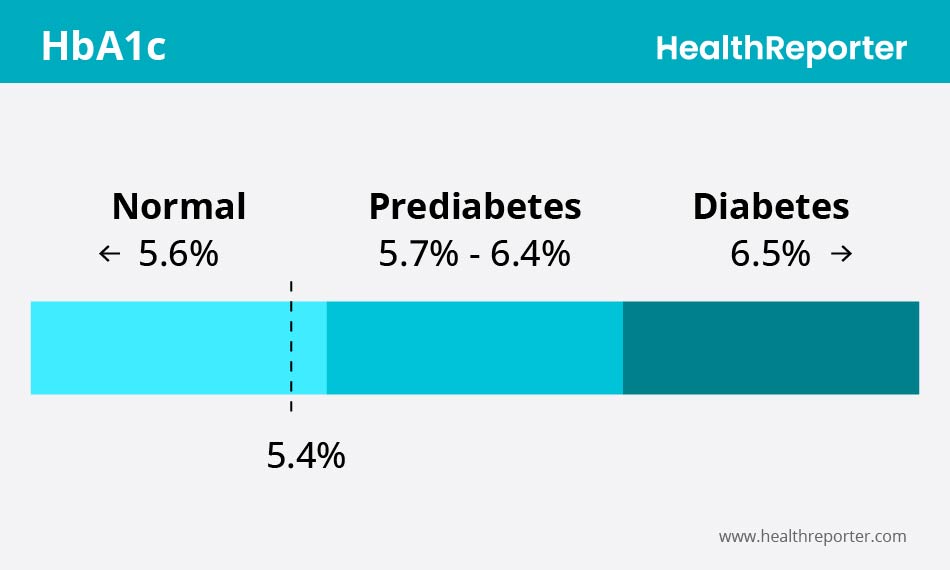
What Does Hemoglobin A1c 5.4 Mean?
A hemoglobin A1c result of 5.4% is considered to be within the normal range.
This level means that only 5.4% of your blood contains sugar, which is great for preventing diabetes mellitus. Anything between 4.6% and 5.6% on the test shows that you have had strong blood sugar control over the past three months, so it’s important to stay in this target range.
However, exceeding this number could increase your risk of developing diabetes. Make sure to perform continuous glucose monitoring when maintaining your long-term health. You can go to the doctor’s office for blood tests, which require a blood sample from a finger or your arm.
Below, you’ll find a table containing set measurements:
| HbA1c | Percentages |
| Normal ✅ | 3.5–5.6 |
| Prediabetes ❌ | 5.7–6.4 |
| Diabetes ❌ | 6.5+ |
How to Maintain Normal A1c Levels
There are many ways to maintain average blood sugar levels. Making healthy lifestyle changes is the first step to looking after your body in the long term. Remember that red blood cells live for 3 months,1 so you need to get a hemoglobin A1c test regularly when building healthier habits.
Let’s take a look at 3 ways you can maintain the average blood sugar level:
#1 Clean diet
Eating clean food – fresh, whole, not packaged food – is known to prevent high blood sugar.2 This includes fiber, vitamins, and protein-rich meals that strengthen the heart. A blood test can immediately tell whether you’re consuming processed foods, so always consume a balanced diet containing essential nutrients.
Some good ingredients comprise chicken, whole grains, plain yogurt, eggs, legumes, nuts, leafy greens, seed butter, fatty fish, and fruits. There are clinical trials that state how fresh food helps people prevent and manage diabetes complications in the future.2
The Klinio app is recommended for prediabetes and diabetes monitoring and prevention, even if your hemoglobin levels are normal. This personal diabetes assistant focuses on your meals, water intake, exercise routine, and hemoglobin A1c results to help you feel healthy.
Klinio also offers recipes with precalculated calories, macronutrients, and portions. You can find a meal plan that suits your dietary preferences, including any personal restrictions like allergies.

- Personalized and diabetes-safe meal plan
- An integrated shopping list that matches the meal plan
- No-equipment home workouts
- All-in-one health and progress tracker
- Detailed activity log
#2 Enough exercise
Getting enough physical activity, like going for a run or walk, can stop glucose from building up in red blood cells.
Exercise makes the body more sensitive to insulin3 – an important hormone that helps blood sugar enter your fat, muscle, and liver cells for energy. As you might already know, too much of this sugar increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain blood disorders.
One study found that 30 minutes of walking a day, combined with a clean diet, reduces the risk of diabetes by 58%.4 You don’t need to do much when it comes to regular exercise. Even a simple walk every morning is a good way of maintaining your optimal A1c levels.
The goal is to get at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity per week.5 This should keep your A1c within the target range, which is great for preventing any long-term health conditions.
If you can’t exercise regularly, talk to your healthcare provider about finding the right exercise routine. For example, people with joint problems such as arthritis may need extra care when going out for long walks or runs.
#3 Reduce stress
High levels of stress may change your A1c test result.
Research has found that stress may increase blood pressure, blood sugar, and insulin resistance.6 All of these factors are harmful to diabetes management, so it’s important to reduce stress and anxiety by finding calming techniques.
You can take regular breaks, make time for your hobbies, try deep breathing exercises every morning, and introduce new habits in your daily routine. If you’re concerned about your blood sugar levels, get an A1c test every 3–6 months to ensure the red blood cells are healthy.
Those with anxiety can also seek professional help to cope better. Talking about your health concerns could reduce any subconscious stress, which hugely impacts diabetes prevention.
Other ways to maintain optimal A1c levels
Some people find other ways to maintain A1c levels, like getting an oral glucose tolerance test to measure their body’s response to glucose. However, if you don’t want to do more tests, the American Diabetes Association has recommended some great at-home tips.7
Of course, you don’t need to complete all of these, but it’s worth doing as many as you can to lower those blood sugar levels.
Here are a few things you can do:
- Quit smoking
- Drink more water throughout the day
- Reduce your meal portions
- Go for regular walks
- Limit your alcohol intake
- Aim to lose excess weight
- Eat more plant-based foods
- Reduce your intake of carbs
FAQs
An A1c test showing 5.4% is equivalent to a blood sugar reading of 108.28mg/dL. This means you’re healthy and not likely to get impaired glucose tolerance (prediabetes). Just make sure to look after your body when maintaining that reading on a hemoglobin A1c test.
It’s recommended that you avoid high-sugar foods in general. While these are acceptable in moderation, the key to good health is consuming clean foods. For those with a 5.4% A1c test result, limit how much sugar you consume to avoid needing a diabetes treatment plan.
People with diabetes need to test every 3 months for effective diabetes management. However, if your hemoglobin levels are at the normal average level, you can test once a year. Always consult with your healthcare provider about testing how much glucose is in your system.
- Blood. (n.d.). Medlineplus.gov., https://medlineplus.gov/blood.html#
- Sami, W., Ansari, T., Butt, N.S. and Hamid, M.R.A. (2017). Effect of diet on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. International Journal of Health Sciences: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5426415/
- Venkatasamy, V. V., Pericherla, S., Manthuruthil, S., Mishra, S. and Hanno, R. (2013). Effect of Physical activity on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical & Diagnostic Research: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3782965/
- Your Game Plan to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes. (2017). National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-type-2-diabetes/game-plan
- Get Active! (2021). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/active.html#
- Stress and high blood pressure: What’s the connection? (2021). Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/stress-and-high-blood-pressure/art-20044190#
- Diabetes Prevention (n.d.). American Diabetes Association: https://diabetes.org/tools-support/diabetes-prevention

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: 



