An A1c test measures the percentage of blood cells in your body with sugar-coated/glycated hemoglobin. The test results determine whether your blood sugar levels are normal or if they indicate prediabetes or diabetes. Keep reading to learn what your results mean using the A1c chart.
A1c Chart: Explanation, Levels, and Categories

Are you unfamiliar with the A1c test?
If so, you need to know how to interpret and understand your test results to take the appropriate action. Your doctor will talk you through your results, but the numbers can initially seem overwhelming. With the help of the A1c chart, you can get to grips with your reading.
Thank you for your answer
Health Reporter Surveys
A1c is a simple blood test requiring a visit to the doctor. It can tell you a lot about your health as it checks for prediabetes, as well as type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. It also plays a vital role in diabetes management and helps mitigate future diabetes complications.
In this article, we explain what the A1c chart is and what its results mean.
What Is an A1c Chart, and What Does It Measure?
The A1c chart outlines the results of an A1c test. The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or glycated hemoglobin test, shows the estimated average glucose in your blood over the past few months.
The chart shows the percentage of red blood cells with glucose-coated hemoglobin based on estimated average glucose values. The numbers show if your blood glucose levels fall into the normal, prediabetes, or diabetes range. Reading the chart can help you understand your results.
What Are the Levels of the A1c Chart?
The A1c chart has three levels: normal, prediabetes, and diabetes. Your A1c test results give a percentage, and that percentage falls into one of the three categories. The scale also shows how close you are to the other categories and your risk for developing prediabetes or diabetes.
The percentage shows how much of the hemoglobin in your blood is saturated with sugar.
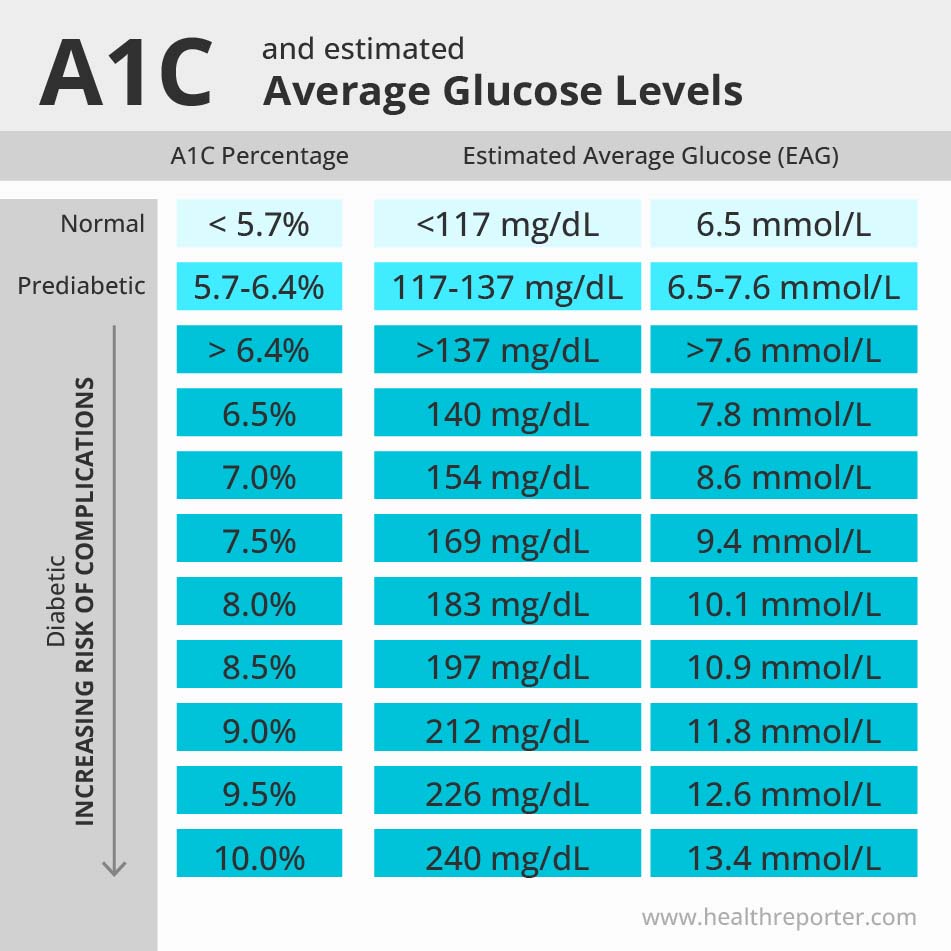
Normal
A normal A1c level is below 5.7%.
So, readings from 4.0% to 5.6% are normal. It means your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months are within the normal range. It indicates good blood sugar control and suggests that you are not currently at risk for developing prediabetes or diabetes mellitus.
A1c levels can fluctuate due to natural changes in your blood glucose levels. It’s important to keep your average blood glucose levels within the target range to stay healthy. If you exceed the normal level and your result is 5.7% or over, you could increase your prediabetes and diabetes risk.
Prediabetes
The A1c level indicating prediabetes is 5.7% to 6.4%.
Prediabetes means your blood sugar levels are higher than normal. It is not high enough for you to receive a diabetes diagnosis, but prediabetes is a serious medical condition that requires a treatment plan to reduce it from further developing into diabetes. The higher the number, the greater your diabetes risk.
If you are worried about developing prediabetes, it is important to visit your doctor for blood tests. Early diagnosis is vital for diabetes prevention. It does not usually have symptoms, but your doctor can quickly discover if your average blood sugar level is higher than normal using an A1c test.
Prediabetes risk factors include family history, genetics, being overweight, physical inactivity, and being over the age of 45.
Diabetes
A diabetes A1c level is 6.5% or above.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that causes high blood glucose levels. There are two main types – type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes impairs the way your body makes and uses insulin.
The longer you have diabetes and poorly controlled blood sugar levels, the higher your risk of diabetes complications, such as heart, digestive, and kidney diseases. You should visit your doctor as soon as possible for a blood test if you think you might be at risk of diabetes.
You can also look out for diabetes symptoms, including the following:
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Feeling very thirsty (polydipsia)
- Feeling hungry, despite eating enough food (polyphagia)
- Feeling tired
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Unexplained weight loss
- Numbness, pain, or tingling in the hands and feet
The three p’s (polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia) often co-occur. They are the three most recognizable symptoms of undiagnosed diabetes.
A1c Chart by Age
Age is an important factor affecting A1c levels. Target A1c levels vary between individuals, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach for glycemic targets. The normal range is 4.0% to 5.6%, but there are some recommended targets for people with diabetes to meet.
For most people, the American Diabetes Association recommends:
Children and teens: 7% or lower
Adults: Below 7%
How Often Should I Measure My Glycated Hemoglobin Levels?
How often you should measure your glycated hemoglobin levels depends on your A1c test result. Whether you have prediabetes, diabetes, or normal blood glucose levels will determine the frequency of the A1c test to ensure you improve or maintain your average blood sugar.
You should get a periodic A1c test if you’re an adult over the age of 45 or if you are overweight with other risk factors for diabetes. If you have a normal hemoglobin A1c test but are at increased risk, your healthcare provider will usually recommend that you get tested every 3 years.
A prediabetes diagnosis will require a repeat test, usually every 1–2 years. In the meantime, your doctor can advise you on lifestyle changes to get your average blood glucose level back into the healthy range. This involves creating healthy habits, like exercising and eating a healthy diet.
If you have diabetes, you will most likely need an A1c test twice per year. If you struggle to keep your blood sugar level within the target range, you might need to test four times a year. Your healthcare team will create a diabetes management plan so you can control your condition.
Many factors can impact your A1c test results, such as medications, dietary supplements, stress, sleep deprivation, and iron deficiency. If you are unsure about your result due to these other factors, you may need a repeat test to be sure.
How Does the A1c Test Work?
The A1c test is a blood test you get at the doctor’s office. A member of your medical care team takes a blood sample, either from a vein in your arm or with a finger prick test using a lancet needle. It takes a few minutes, and the blood sample is sent away for analysis.
The test measures the amount of red blood cells with sugar-saturated hemoglobin. The results appear as a percentage, and your doctor uses it to review your average blood glucose levels from the previous 2–3 months. It confirms if your blood glucose is within healthy levels.
Hemoglobin is a protein in your red blood cells that works to carry oxygen throughout your body. When glucose enters the bloodstream, it binds with hemoglobin. The more glucose you have in your system, the more glycosylated hemoglobin you have. High levels can indicate diabetes.
A1c testing is used to diagnose prediabetes and type 1 and 2 diabetes. Regular testing is also used as part of a diabetes treatment plan. It aids diabetes control by monitoring a person’s blood sugar levels to ensure their treatment plan is working effectively.
People with diabetes can also use a blood glucose meter at home.
FAQs
A good A1c for adults is between 4.0% and 5.6%. An A1c test reading below 5.7% means your average blood glucose levels are within the normal range. People with prediabetes and diabetes have higher blood glucose. The recommended goal for most adults with diabetes is an A1c test below 7%.
According to the American Diabetes Association, older adults who are generally healthy should have glycemic targets of 7.0% to 7.5% on an A1c test. Those with chronic illnesses and other health conditions may have a higher A1c result.
A good A1c for kids with diabetes primarily depends on the age group. Generally, the target range for children and teens is an A1c of 7% or lower. A doctor will continuously monitor A1c levels and recommend a good target and treatment goals based on age and overall health.
A Word From Our MD
The A1c test is one of the most popular tests in diabetes care.
Diabetes is a lifelong condition that occurs when too much sugar is in your bloodstream. It can cause tiredness, weight loss, excessive thirst, increased urination, and swelling in the legs and feet. It can affect your day-to-day life, but you can keep it under control with a proper management plan.
A diabetes treatment plan usually involves regular check-ups, medication, and dietary changes. Good nutrition is essential for supporting glycemic control. For example, processed, high-carb foods, like white bread and french fries, can trigger rapid spikes in your blood sugar.
Getting plenty of exercise is another way to curb high glucose. Physical activity makes your body more reactive to insulin – the hormone that helps your cells use glucose for energy. You could go for morning walks or take up running to support your treatment goals.
If left untreated, diabetes can cause many long-term health problems. It may cause blindness and nerve damage and increase your risk of cardiovascular disease. The A1c test is an essential device for controlling your health.
Conclusion
The A1c chart is a vital part of diabetes care and prevention. It allows doctors to catch prediabetes as early as possible so those with higher blood sugar levels can begin a treatment plan to prevent full-blown diabetes. It also helps manage diabetes in those who receive a diagnosis.
So, if you think you are at risk, speak to a healthcare professional about taking the hemoglobin A1c test.

- Personalized and diabetes-safe meal plan
- An integrated shopping list that matches the meal plan
- No-equipment home workouts
- All-in-one health and progress tracker
- Detailed activity log

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: 



