11 Most Popular Types of Keto Diet: Which One Is for You?
Keto diets are low-carb, high-fat eating plans that can help you lose weight and improve your health. Explore the different types of keto diets and learn how to choose one that’s right for you.

The ketogenic diet, mostly known as the keto diet, involves drastically reducing your carb intake and instead focusing on eating high-fat and moderate-protein foods. It’s an effective weight-loss diet and can also provide other health benefits, such as improved blood sugar levels and increased energy.
Reducing carbs brings your body into a metabolic state called ketosis – the breakdown of body fat into ketones, allowing your body to run mostly on ketones rather than glucose. This improves your body’s efficiency at burning fat for energy.
There are different ways to achieve ketosis. That is why there are different types of keto diets to choose from, depending on your specific needs and goals.
Each keto diet has its own set of guidelines you should follow to attain the best outcomes. We will go over each type in depth so you can determine which one is ideal for you.
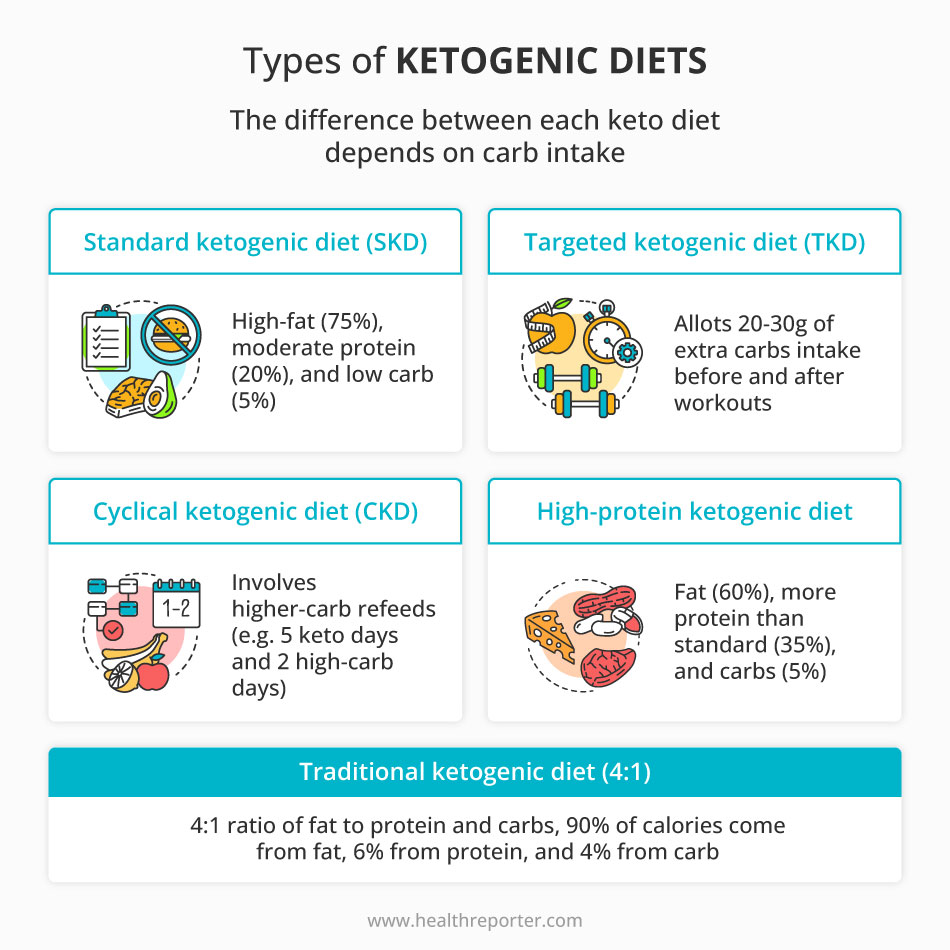
11 Most Popular Types of the Keto Diet
Early research suggests that a low-carb, high-fat diet may help treat certain cancers, diabetes, ADHD, and other illnesses. Below are the 11 most common types of the ketogenic diet.
#1 The standard ketogenic diet (SKD)
The standard ketogenic diet (SKD) is one of the most common keto diets. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that has helped people lose weight and manage their health concerns.
The SKD emphasizes eating a high volume of fats and proteins while reducing carbohydrates in your daily diet. It’s 70% fat, 20% protein, and 10% carbs. This assists in putting the body into ketosis, a state in which it burns fat for energy rather than glucose from carbohydrates.
The standard ketogenic diet is also known for its wide range of health benefits, including improved mental clarity and focus, increased energy levels, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
#2 The targeted ketogenic diet (TKD)
The targeted ketogenic diet (TKD) is a variation of the keto diet that allows the consumption of a high-carb diet needed for workouts.
The targeted keto diet aims to maintain ketosis while providing additional energy for workouts. This can benefit those looking to increase performance and those trying to lose weight and exercise regularly.
With careful planning and monitoring carbohydrate intake, the targeted ketogenic diet can provide athletes and fitness enthusiasts with the energy they need to perform at their best during intense physical activity.
#3 The cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD)
The cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD) includes cycling between times of low-carb eating and higher-carb refeeds. This cyclical increment or decline in carb intake is called carb cycling. It offers you the power for meal planning as you set yourself up for success on this low-carb diet.
Carb cycling can help promote weight loss and muscle growth and help treat certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and epilepsy.
#4 The high-protein ketogenic diet
The high protein ketogenic diet (HPKD) is the same as the standard keto diet in that fat accounts for most of your daily macronutrient consumption. However, as the name suggests, this type of keto diet involves consuming a higher percentage of protein.
Its macronutrient ratio contains 60–65% fat, 30% protein, and 5–10% carbs.
A high-fat, low-carb diet like this helps regulate your blood sugar levels, resulting in longer-lasting energy and stabilizing hunger hormones and cravings.
This keto diet has been proven to help lose weight and improve general health.
#5 The traditional ketogenic diet (4:1)
The traditional keto diet, or the classic keto diet, was created in the 1920s to treat children with epilepsy. During the research, children who remained more in ketosis had diminished seizures.
In terms of food choices, the traditional keto diet only allows 1 gram of protein and carbohydrates for every 4 grams of fat. This 4:1 ratio means that 80% of your calories should come from fat and the rest from carbohydrates and protein.
This keto diet is good for raising ketone levels but is very limited. It’s best recommended by a specialist, for example, for epilepsy or cancer.
#6 The vegetarian and vegan keto diet
While keto is most often associated with animal-based foods, it can be modified to suit plant-based lifestyles, including vegetarian and vegan.
The vegetarian and vegan keto diet is suitable for those who follow a primarily plant-based lifestyle and still want to reap the benefits of the ketogenic diet.
Vegans eat solely plant-based foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and grains, and avoid animal-based foods, such as meat, poultry, eggs, and dairy. Vegetarians can eat animal byproducts, such as eggs, dairy products, and honey, that don’t come from animal slaughtering.
You can achieve ketosis by consuming high-fat plant-based foods, such as coconut oil, avocados, seeds, and almonds.
The vegetarian and vegan keto diet has the same macronutrient ratios as standard keto, allowing you to stay in ketosis and lose weight while adhering to your dietary needs and lifestyle preferences.
#7 The Mediterranean keto diet
The Mediterranean keto, recently dubbed keto 2.0, combines two popular eating styles: sticking to the macros of standard keto while emphasizing the components of the Mediterranean diet, such as fatty fish and olive oil.
Unlike the standard keto diet, which does not specify which fats to prioritize, the Mediterranean keto diet stresses alternatives like monounsaturated fatty acids, which may drastically reduce LDL cholesterol, and omega-3s, which are anti-inflammatory.
The keto 2.0 diet is for people who want a flexible, sustainable, and long-term healthy diet, with a focus on Mediterranean components such as whole-wheat bread, brown rice, and plenty of vegetables, fruit, and beans.
#8 The keto-paleo diet
The practical approach to the keto-paleo diet, also known as the ketogenic paleolithic diet, mixes the standard keto macro ratios with paleo diet food selection. The emphasis is on eating healthy, natural meals, with animal products providing most of the energy.
Grain (cereals and bread), vegetable oils, dairy products, refined sweets, and processed foods are all avoided.
The diet has been studied as a treatment for type 1 and 2 diabetes and has shown promising results.
The keto-paleo diet may offer potential health benefits, such as weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation. However, it may also be restrictive and challenging, as it eliminates several food groups, such as dairy products or grains.
#9 The MCT keto diet
The MCT keto diet is similar to the standard keto diet but includes medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). MCT keto is designed to improve mental performance and the benefits of keto by eating healthy fats.
This means you’ll consume the same meals as standard keto, but add MCT oil to your coffee, mix it into your salad dressing, or blend it into your post-workout protein shake or smoothie.
The MCT keto diet boosts your fat consumption, promotes ketone production, and helps you reap the benefits of mental clarity throughout the day.
#10 The well-formulated keto diet
The well-formulated ketogenic diet emphasizes balancing electrolytes and minerals lost through sweat. This is great for those who do a lot of HIIT workouts or sweat a lot. This diet allows you to load up with foods that will replenish lost minerals and provide the energy you need to maintain your workout regimen.
On this diet, you eat the same foods as standard keto, with the same macronutrient ratios, but prioritize electrolyte-rich meals, such as those high in magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
This includes consuming more green vegetables, seeds, nuts, and plain full-fat dairy, such as cottage cheese. Ensure to drink water and other keto drinks throughout the day.
The well-formulated keto diet helps hydrate your body and combat bloating and fatigue that comes with dehydration. Increased hydration has also been shown to promote weight loss.
#11 The lazy keto diet
This type of diet is designed for those who want to reap the benefits of the ketogenic diet without counting calories. The lazy keto diet involves reducing your carb intake and eating high-fat, moderate-protein meals without worrying about tracking your macros.
It also allows for more flexibility than other types of keto diets, so it may be a good choice for those who want to start a new diet without feeling overwhelmed by strict rules and regulations.
As long as you keep your carbohydrate intake low enough and don’t go overboard on protein, you should get similar benefits to standard keto.
What Is Considered Keto?
A ketogenic diet is as low-carb as you may go. Most people break it down by macronutrient ratio, which is the percentage of protein, carbohydrates, and fats consumed daily. A keto diet generally includes 15–25% protein, 5–10% carbs, and 65–80% fat.
A ketogenic diet aims to help you reach ketosis, where your body uses stored fat for energy. Your liver then produces ketones as it breaks down the fats. These ketones are what your body uses for energy.
Keto might be similar to Atkins and other low-carb diets, but its main purpose is keeping your body in ketosis by restricting carb consumption.
How to Choose the Right Keto Diet for You
There are many factors to consider when choosing a keto diet. First, you need to consider your goals and lifestyle. Do you want to lose weight? Are there any food sources that you avoid? Or do you have any food sensitivities?
Having these questions at the top of your priority list can help you sample the different types of keto diets and decide on the one that meets your needs.
If you’re new to keto, using keto apps can help you figure out which keto diet is best for you.
It’s also important to approach any ketogenic diet cautiously and make sure it’s appropriate for your health needs. Working with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help ensure that you are following a safe and effective nutrition plan.
FAQs
The standard ketogenic diet is the most effective keto diet. Its macros are 75% fat, 20% protein, and 5% carbohydrates. This means limiting your carbohydrate intake to 20–30 grams per day.
The most effective ketogenic diet is the one that meets your goals, matches your dietary requirements, and is one you can stick to in the long term. It can also depend on your medical conditions and preferences.
The semi-keto diet allows you to eat more carbohydrates than other keto diets. You can increase your carbohydrate intake to moderate levels of about 50 to 100 grams per day. It also allows for a wider variety of foods, making it easier to stick to than strict diets that restrict certain food groups.
A Word From a Nutritionist
Following a keto diet requires restricting carbohydrates. Start with 20–30 grams of carbohydrates per day. Also, make sure you understand which foods are high in carbohydrates, fat, and protein to make the best choices.
It’s also essential to consume plenty of keto veggies to ensure you are getting all of your vital vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Choose non-starchy vegetables high in nutrients, such as kale, spinach, broccoli, asparagus, peppers, and mushrooms.
Since the keto diet increases your fat intake and reduces carbohydrates, choosing healthy fats from high-quality animal and plant sources, such as avocado, olive, or coconut, is critical.
Whichever form of keto you choose, remember that it might take time to see results. If you are not overweight, you may not lose as much weight. The more weight you have to lose, the quicker you will lose it in the beginning.
It’s essential to note that slow weight loss is healthier, more likely to stick, and sustainable. Be patient with yourself, and don’t give up on the keto diet.
Conclusion
The keto diet consists of eating low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein foods. However, these proportions can change depending on the type of keto diet you choose. The most common are the classic, standard, cyclical, MCT, and lazy keto diets. The ideal type to choose depends on your nutritional needs.
Consult your nutritionist or specialist before starting any of these weight loss diets. Your doctor will be able to advise you if this diet is good for you and won’t cause any medical conditions or deficiencies.

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: 








