Magnesium for Weight Loss: A Dietitian’s Take
Magnesium is an essential mineral used to regulate bodily functions such as energy production and muscle contraction. This article will assess how magnesium affects weight loss, its health benefits, and its side effects.
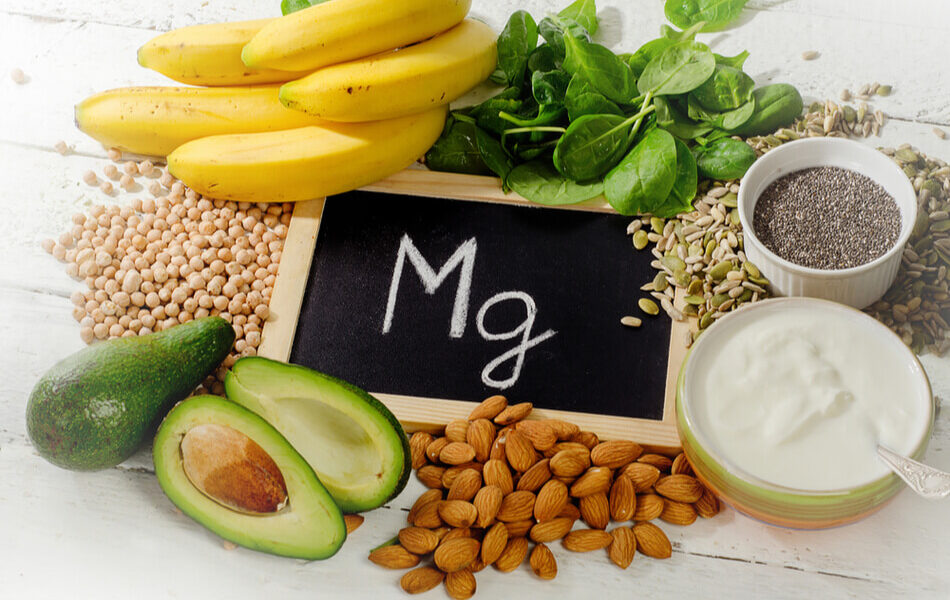
Magnesium is a crucial mineral that the body needs to function correctly. It is among the essential electrolytes the body requires as cells use magnesium to synthesize enzymes and initiate chemical reactions in the body.
Though magnesium is present in many food groups such as nuts, leafy greens, beans, and seeds, magnesium deficiency is common in people. Despite its numerous associated health benefits, you might be wondering whether you can use magnesium for weight loss.
This article will assess magnesium’s functions and health benefits, its effect on weight loss, and the possible associated health risks.
Magnesium for Weight Loss – Does It Help?
Magnesium alone does not lead to weight loss, but it normalizes metabolism when incorporated into a healthy diet, helping one lose excess weight.
Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating the glycemic response and blood sugar levels in obese, overweight, and type 2 diabetes patients. This regulates insulin levels, subsequently leading to weight loss.
Magnesium also boosts cellular energy production, increasing the overall body metabolism and helping one lose weight.
It also reduces bloating and water retention, alleviating menstrual symptoms among ladies. Magnesium citrate is also a stool softener, helps one lose water, and improves hormonal balance and energy production, thus helping one shed excess abdominal fat.
When you have low magnesium levels, you experience constant fatigue and low energy levels, which subsequently cause weight gain.
What Is Magnesium?
Magnesium is an important mineral that plays a role in over 300 enzyme reactions in the body. The human adult body has 25g of magnesium. 50–60% of it is stored in bones, and the rest is in body fluids and muscles.
It helps the body in bone development, muscle contraction, conducting nerve impulses, and transporting calcium and potassium throughout the body. Research also suggests that magnesium plays a role in DNA synthesis and normal heart rhythm.
Magnesium deficient people experience a range of health complications, and it is crucial to get the daily recommended dose for healthy bodily functions. If you cannot get sufficient magnesium doses through diet, opt to get a magnesium supplement under a doctor’s prescription.
Magnesium-rich foods
You can meet your daily recommended magnesium intake by consuming magnesium-rich foods. These include:
- Avocados
- Nuts
- Legumes
- Seeds such as chia, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds
- Whole grains
- Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel
- Leafy green vegetables, such as kale, spinach, lettuce, cabbage, and microgreens
- Bananas
- Tofu
- Low-fat dairy products
- Dark chocolate
If you have a magnesium deficiency, you may get more magnesium through supplements. However, you should get enough from your diet if you have no major health problems.
10 Types of Magnesium
There are 10 magnesium types present in food products and dietary supplements. These include:
- Magnesium citrate
- Magnesium sulfate
- Magnesium oxide
- Magnesium taurate
- Magnesium lactate
- Magnesium glycinate
- Magnesium chloride
- Magnesium malate
- Magnesium orotate
- Magnesium L-threonate
Each magnesium type has different properties depending on medical uses, potential side effects, and how easily the body absorbs them.
Most magnesium types are available in supplements and are sold in different delivery systems as pills, powders, or gummies. The delivery system doesn’t matter, but you can opt for easily absorbed types, such as magnesium citrate.
Magnesium citrate is the most common type of magnesium, usually found in various supplements. It is also used to treat constipation due to the laxative effect.
Magnesium and Water Retention
Increasing magnesium intake may help reduce water retention. It also helps alleviate premenstrual syndrome and bloating. If you notice some parts of your body, such as your hands or feet, swollen, it could be due to fluid retention.
Magnesium affects the hormonal balance of fluids, thus allowing the body to get rid of excess fluids. This reduces fluid buildup in the body, helping you achieve a healthy weight.
The most common type of magnesium used to get rid of water retention is magnesium oxide (MgO).
4 Magnesium Benefits for Weight Loss
Magnesium is present in certain foods, and it has numerous beneficial effects on weight loss. It helps produce energy and boost athletic performance. This mineral is essential for bodily functions and helps prevent chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Alzheimer’s.
Below are some of the benefits of magnesium on weight loss.
#1 Improves sleep quality
Magnesium supplements are used as a natural remedy for sleep-related issues like insomnia. This is because they help regulate the neurotransmitters involved in sleep. Chemically, it activates the parasympathetic nervous system, getting you calm and relaxed.
A systematic review on magnesium supplementation for adults suggests that people with enough magnesium in the body fall asleep faster by an average of 17 minutes. It also regulates melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
It helps relax muscles and quiet the nervous system, thus preparing the body for sleep. Sleep deprivation is associated with gaining body weight and making your body metabolically groggy. One feels hungrier and less satisfied after meals leading to eating habits.
Sleep deprivation causes an increased risk of low insulin sensitivity, thus making it hard for your body to process fats from the bloodstream. The body ends up storing them as fats.
#2 May help boost athletic performance
During exercise and strenuous activities, your body needs magnesium more than when it is resting. When exercising, your muscles use magnesium to move glucose around the body and dispose of lactic acid that builds up during exercise.
It also helps improve the exercise performance of old individuals looking to lose weight through working out. Magnesium deficiency leads to muscle soreness, seizures, fatigue, and cramps affecting athletic performance.
#3 Natural mood and energy booster
Magnesium is a natural mood and energy booster that helps treat anxiety and depression disorders. Randomized studies in a controlled trial showed that magnesium alleviates depressive symptoms in as low as two weeks.
Magnesium boosts the mood partly because of activity in the glands that regulate the body’s reaction to stress.
#4 Regulates blood sugar
Magnesium is crucial in blood sugar management. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Most people with type 2 diabetes have magnesium deficiency as they lose a high amount of this nutrient through urine.
A meta-analysis among a control group of patients showed that regular magnesium supplementation reduced chronic inflammation, led to fat loss, and helped lower the body mass index. All this helps regulate blood sugar and lower blood pressure.
By assisting in regulating blood sugar levels, magnesium helps one lose weight. These effects depend on how much magnesium you are getting from food.
Magnesium supplements also do not improve blood sugar levels in diabetes patients that are not magnesium deficient.
Possible Side Effects of Magnesium
Most people who take magnesium supplements do not experience adverse side effects. However, high magnesium levels can cause gastrointestinal problems such as constipation, abdominal cramping, nausea, and diarrhea.
Taking too much magnesium causes buildup in the body that can cause low blood pressure, loss of control in the central nervous system, urine retention, irregular heartbeat, slow breathing, or even a coma.
People with kidney issues are more likely to experience adverse health effects from taking magnesium supplements. Kidneys that don’t function properly have problems in clearing magnesium from the system, and taking more supplements will allow magnesium to build up to toxic levels.
It may also be unsafe when taking diuretics, heart medications, and antibiotics. Check with your healthcare provider first to assess your health condition before opting for any magnesium supplements.
FAQs
Below are some of the frequently asked questions concerning magnesium for weight loss.
Yes, magnesium helps with bloating. It alleviates gastrointestinal bowel syndrome, which has symptoms like diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal cramping, constipation, and bloating.
Increasing the intake of magnesium-rich food helps minimize these symptoms and improve gut health.
As a mineral, magnesium has no calories that can lead to weight gain. It improves your energy levels, sleep patterns, and overall mood, contributing to weight loss. However, magnesium deficiency can interfere with normal body functions. It causes insulin resistance which causes weight gain. Most obese people and overweight people have a magnesium deficiency.
Yes, magnesium speeds up metabolism. It is responsible for many chemical reactions essential for energy production and metabolism in the body. Magnesium is also necessary to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a coenzyme necessary for transporting energy in cells. Increased metabolism accelerates weight loss and can help you shed excess belly fat.
Healthy male adults should consume 400–420mg of magnesium a day, whereas healthy adult females should consume 310–320mg of magnesium a day. For pregnant women over 18 years, the intake should be increased to 350–360mg a day.
A Word From Nutritionist
Having enough magnesium in your diet is paramount for improving overall health. However, it is not a magic solution for weight loss; sustainable weight loss results from following a healthy eating plan and a regular workout routine.
Many people do not get the daily recommended intake of magnesium. You can improve your daily magnesium uptake by consuming magnesium-rich foods or taking magnesium supplements.
When taking supplements, avoid going beyond the recommended dosage. Though magnesium toxicity is uncommon, taking very high doses can cause obvious signs like nausea, abdominal and leg cramps, and diarrhea.
Magnesium interacts with medications like antibiotics and diuretics. This makes it necessary to consume these supplements under the supervision of a healthcare professional to assess the interaction of magnesium with other medicines you may be using and its effects on any underlying conditions you may have.
Conclusion
Magnesium is essential for numerous body functions. It is also associated with a reduced risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other conditions. You can get it from dietary sources or supplements.
Though magnesium on its own does not lead to weight loss, it supports various activities in the body that result in weight loss. The best way to lose weight is by making lifestyle changes such as starting regular exercise and healthy eating habits.
Despite all the benefits of magnesium, speak to a licensed healthcare practitioner for medical advice before using magnesium for weight loss.

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: 








