Is Halibut Healthy? Nutrition, Calories, and Mercury Content
Whether served as fish tacos, baked halibut, or even grilled fish steaks, many wonder about the health benefits and drawbacks to eating halibut.

Due to its relatively mild flavor, halibut is very versatile for your cooking needs. It is also packed with nutrition, including protein, omega-3 fats, and much more.
You may be wondering, are there any drawbacks to eating halibut?
Is Halibut a Healthy Fish?
Overall, halibut is a healthy fish that is high in vitamins, minerals, omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and much more. However, due to the mercury content, it is recommended to consume halibut once a week.
What Are the Nutritional Differences Between Salmon and Halibut?
| Calories/Nutrient per 100g | Salmon | Halibut |
| Calories (kcal) | 208 | 186 |
| Fats (g) | 13.4 | 13.8 |
| Protein (g) | 20.4 | 14.4 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 55 | 46 |
| Sodium (mg) | 59 | 80 |
Salmon is another fatty fish very similar to halibut in that they are both rich in omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and vitamins and minerals.
A primary difference between them is that salmon is much lower in mercury than halibut fish. Therefore, salmon can be consumed two to three times a week, while halibut can just be consumed once a week and with no other fish, according to the FDA and EPA guidelines.
5 Halibut Health Benefits
Halibut is a healthy fish, rich in vitamins, minerals, and much more. Let’s dive into some of the main health benefits and downsides of eating halibut.
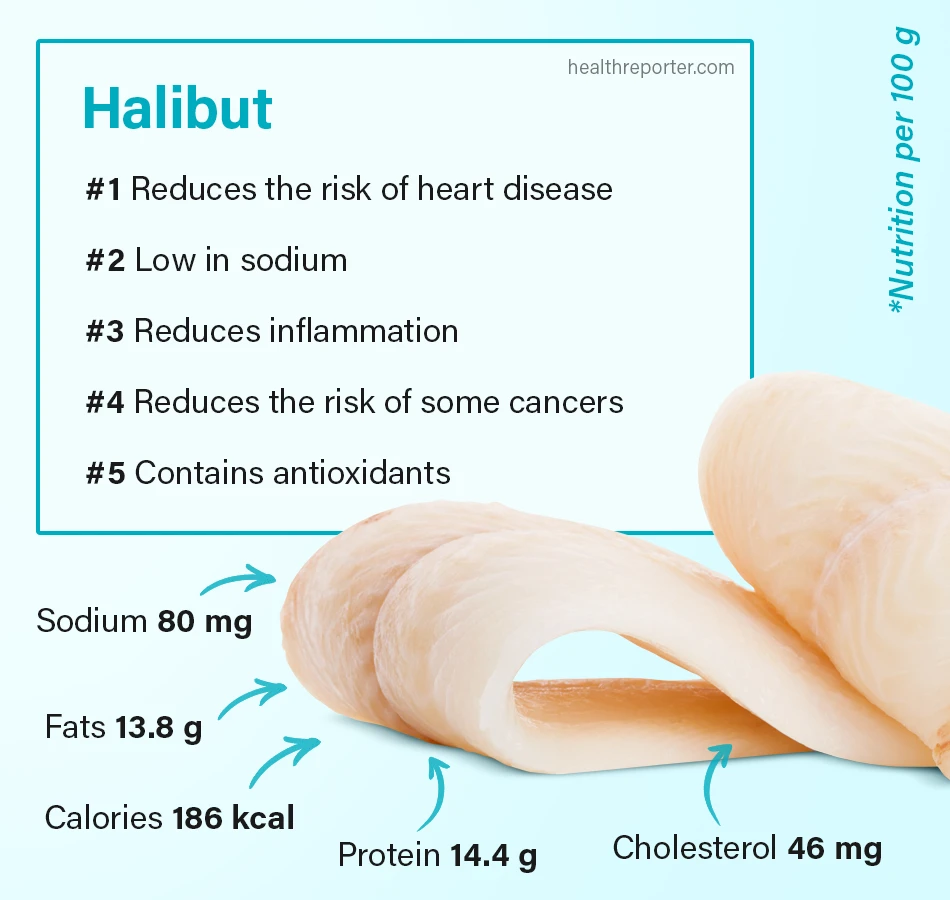
#1 Reduces the risk of heart disease
Halibut is rich in omega-3 fatty acids that are beneficial for your heart and cardiovascular system. Omega-3 fatty acids can decrease blood pressure, reduce triglycerides (a type of fat) in the body, reduce blood clotting, and more.
The Mayo Clinic recommends consuming at least two servings of fish each week to reduce heart disease risk. However, since halibut contains more mercury than a lot of types of fish, only consume halibut once a week and no other fish, as mentioned above.
#2 Low in sodium
A 100g serving of halibut only contains 80mg of sodium, according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) food database. A 100g serving of halibut fish is just under the recommended serving size of 4 ounces.
Therefore halibut fish, whether it is Atlantic halibut or Pacific halibut that live in the North Pacific Ocean, is considered a lower sodium food.
The American Heart Association recommends consuming no more than 2,300mg of sodium daily. However, they advise that closer to 1,500mg per day is even more ideal for overall heart and cardiovascular health.
It is important to note that it is best to avoid over-seasoning your halibut or when you are eating fish of any kind while cooking at home.
If you are ordering halibut while dining out at a restaurant, be mindful of the salt content that many toppings, sauces, and seasonings may contain. If you order a salty halibut dish, try to consume less sodium in the side dishes, or have less salt throughout the rest of the day.
#3 Reduces inflammation
As mentioned above, fish contains omega-3 fats, a specific type of healthy unsaturated fat. The omega-3 fatty acids commonly found in fatty fish, such as halibut, are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
According to the journal Nutrients, omega-3s such as EPA and DHA can help reduce inflammation in the body that often stem from many different disease states, such as atherosclerosis.
#4 Reduces the risk of some cancers
Early research is demonstrating that consuming omega-3s might help reduce the risk of some types of cancer.
A clinical study performed at the Vanderbilt University Medical Center demonstrated a very slight relationship between taking fish oil containing omega-3 fats and decreased colon and rectal cancer development.
However, this study needs to be replicated, and more research must be completed to determine the association between fish oil and cancer risk, treatment, and prevention.
#5 Contains antioxidants
According to the Alaska Seafood Marketing Institute, halibut is a fish rich in selenium, which acts as an antioxidant in the body. Antioxidants are compounds in food that fight free radicals in the body.
According to Harvard Medical School, free radicals are harmful compounds that naturally occur in the body from processes such as exercise. A healthy balance of antioxidants and free radicals in the body can help improve overall health.
Halibut Downsides
While halibut is a relatively healthy fish containing plenty of vitamins and nutrients, it also has a couple of downsides.
#1 High in mercury
According to the FDA, halibut is a white fish that is considered to have only moderate amounts of mercury, whether it is Atlantic, Pacific, wild-caught halibut, or other varieties.
It is classified in the “Good Choice” category by the FDA and EPA with 0.241mg of mercury. Therefore, you can safely consume mercury up to once a week; however, do not consume any other types of fish that week.
#2 Not sustainable
Halibut is not the most sustainable choice when it comes to seafood because it is a slow-growing fish with a long life span, and it is overfished due to its popularity as a food source. It is also particularly vulnerable to overfishing due to its tendency to form large schools, which makes it easy to target large numbers of fish in one area.
Additionally, climate change and ocean acidification are contributing to the decline of halibut populations.
Halibut Nutritional Facts
Halibut is a nutritious fish that many enjoy. So let’s discuss the nutritional information of halibut in detail.
Nutritional table (per 100g)
| Calories/Nutrient | Amount |
| Calories (kcal) | 186 |
| Fats (Total) | 13.8 |
| Protein (g) | 14.4 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 46 |
| Sodium (mg) | 80 |
High in vitamins and minerals
While halibut contains so many vitamins and minerals, some of note are vitamin D and selenium.
Vitamin D is important because it works together with calcium to support strong bones and teeth. Vitamin D is so crucial that it is often added to “fortified” products such as breakfast cereals and milk.
Additionally, selenium is an antioxidant that helps protect cells in the body against damage from free radicals. Also, selenium can help prevent cognitive decline, boost immune health, and much more.
High in protein
Our bodies need many different amino acids to function properly and live. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins that facilitate every chemical reaction in the body.
There are some amino acids that the body can produce itself, but there are nine that we must consume through our food.
According to the Alaska Seafood Marketing Institute, halibut contains all nine essential amino acids and is therefore considered a “complete protein.”
Additionally, a 100g serving of halibut contains 14.4g of protein.
High in fats and calories
Halibut is relatively high in calories and fat and is therefore not considered a lean fish. However, the fat is mainly unsaturated fats such as omega-3 fatty acids, which are suitable for heart health.
When paired with lower-calorie sides such as freshly cooked vegetables, a glass of milk, and some brown rice, your halibut recipes can still be a part of a healthy and balanced meal.
Low in cholesterol
A 100g serving of halibut only contains 46mg of dietary cholesterol.
While the recommendation for cholesterol used to be to consume no more than 200–300mg per day, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans now recommend consuming as little cholesterol as possible.
Therefore, eating fish such as halibut is a great lower cholesterol alternative to eating red meat, such as beef, pork, and lamb.
A Word From a Dietitian
Overall, halibut is a fish that is an excellent addition to your diet because it is very nutritious and versatile. Halibut fish varieties can include Pacific halibut, Atlantic halibut, wild fish populations, and more. In addition, halibut meat is moderately low in mercury and, therefore, is safe to eat up to once a week.
Pair your halibut with whole-grain starch such as brown rice or whole-wheat pasta and a plate full of fresh steamed or roasted vegetables.
Finally, enjoy your halibut with a glass of milk or non-dairy milk alternative to have a really balanced, healthy, and delicious meal.
In general, fish is a wonderful protein source to incorporate into your diet that is rich in omega-3s, such as DHA and EPA, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
FAQs
Eating halibut is good for you due to its nutrient-rich content that is also high in protein and omega-3 fatty acids. However, just like many other fish, it does contain some mercury, so consume it in moderation.
The serving size of any fish, including halibut, is 4 ounces. This is approximately the size of the palm of your hand or a deck of cards.
Since halibut has a moderate amount of mercury, it is safe to eat up to once a week. If you do consume halibut, do not have any other types of fish that week.
Yes, halibut is a cold-water fish often found in the North Pacific or Atlantic oceans.
Conclusion
Halibut, pollock, salmon, and other types of fish, whether in the form of fresh fish or from the grocery store, can be a healthy and delicious part of a balanced diet.
To get all your essential vitamins and minerals, make sure to consume healthy fats, grains, and plenty of vegetables alongside any fish you choose.

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: