How to Stop an OCD Attack: 5 Things to Try Now
Sometimes, the fear can be overwhelming and cause your body to experience negative side effects. An OCD attack is one example of severe dissociation, but how do you stop it? We provide 5 ways you can settle these attacks and be in a calming mindset.
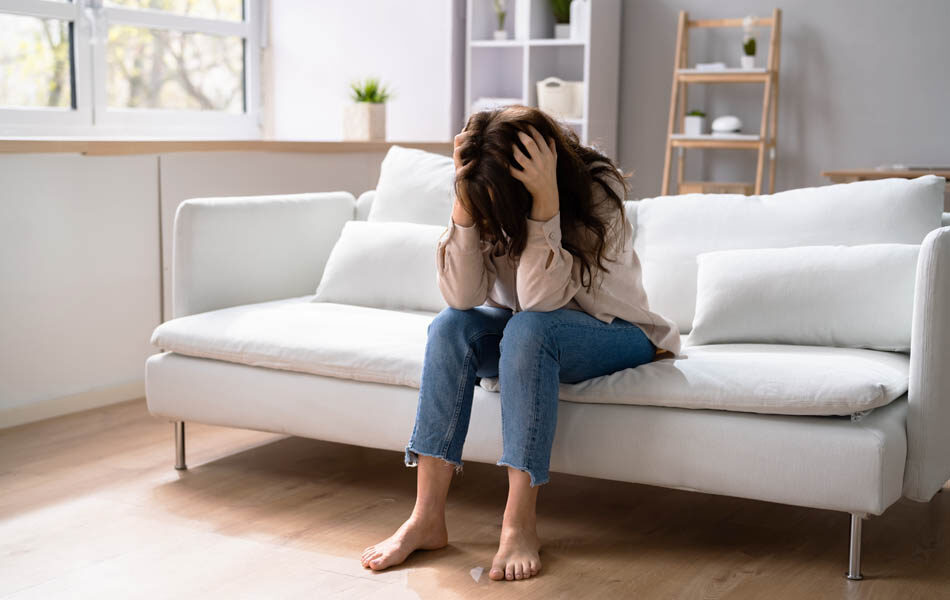

Trying to overcome obsessive thoughts can be challenging.
Certain thoughts and feelings might make the obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) worse. Some people often lose control over their mental state when the overwhelming panic doesn’t settle down. In time, attacks become more demanding, which can really take a toll on your health.
Finding ways to prevent these attacks could help you effectively manage OCD. When the intrusive thought pops into your head, you’ll know exactly what to do next. Commonly prescribed drugs aren’t always the answer to controlling those OCD thoughts.
In this article, you’ll discover 5 ways to stop OCD attacks without medication.
5 Ways to Stop an OCD Attack
- Face your triggers
- Be self-aware
- Find a support
- Utilize relaxation techniques
- Try therapy
How to Stop an OCD Attack? 5 Tried-and-Tested Ways
People will always have different ways of calming intrusive thoughts. One person may feel comfortable talking to a mental health professional, while someone else prefers anti-anxiety medication. It depends on your OCD episodes and response to emotional distress.
Here are 5 ways you could stop OCD attacks:
#1 Face your triggers
Response prevention is a treatment that helps people face their OCD triggers.
You can slowly expose yourself to triggers and learn how to resist compulsive behaviors. For example, making breakfast might be a difficult task if you believe the food is contaminated. Changing the way you think about food could take the stress off by completing small tasks.
One study found that exposure and response prevention can help improve OCD symptoms. Those disturbing thoughts might not appear as frequently when living in the present moment. Always talk to your doctor about effective ways you can start this treatment process.
#2 Be self-aware
There are small things you can do to become more self-aware. Setting boundaries should be one of the first tasks on your list, as this will prevent burnout in the future. You need to understand the emotional limits of your obsessive-compulsive disorder and anxiety.
You could also stay focused by doing some exercise. Consider going for morning runs, slow jogs, or 2-mile walks every day. Studies have shown that exercise pumps more blood to the brain and releases endorphins – hormones that put you in a positive state of mind.
A positive mindset means you can think clearly without losing control. Some other benefits of self-awareness include more confidence, better management of emotions, and higher happiness levels. It’s worth exercising to ease any OCD compulsions.
#3 Find a support system
Support from a family member or close friend could relieve OCD symptoms in the long term. Most people need that support to prevent high anxiety and stress levels. The International OCD Foundation believes support is required to prevent substance-use disorders as well.
Consult with your doctor when finding the best support system.
#4 Utilize relaxation techniques
Deep breathing and meditation could stop an obsessive thought from worsening. Learning more about self-help skills will ensure your compulsions are controlled. Some people believe that sitting in a quiet room and taking deep, slow breaths could relax the mind and body.
Stretching your muscles can also feel good, so stay in a calm environment and stretch the legs, arms, back, and stomach. Focus on your breathing and think about the most important goals in life; a mental health app may come in handy here.
#5 Try therapy
Of course, talking to a therapist isn’t for everyone, but it may help you manage certain emotions and triggers. Being in a quiet space with a trusted professional could dampen your obsessions. Retaining bad thoughts while suffering alone can only increase the risk of OCD attacks.
What Is an OCD Attack?
An OCD attack is a sudden feeling of panic that causes sweaty palms, muscle weakness, troubled breathing, rapid heartbeat, and bad thoughts. You might get extreme fear relating to a certain trigger, which sends both the brain and body into overdrive.
People who experience these episodes usually get panic attack symptoms. They’ll be in a state of panic while struggling to get their breathing under control. This can be especially frightening when in a new environment, making OCD attacks difficult to overcome in a short space of time.
The psychological response to compulsive triggers is fear. Some even report completing rituals like pacing, saying phrases aloud, checking locked doors, and counting numbers. Small habits like this show that the brain is trying to make sense of the fear and why it caused panic.
These attacks might last anywhere between 30 seconds to 10 minutes. It all depends on how the person responds to extreme stress. However, when symptoms become severe over the next few months, it’s important to talk to your doctor about suitable treatment options.
What Causes OCD Attacks?
Small habitual routines that are broken usually cause these attacks. For example, if someone can’t structure their fridge the right way, they might feel a sense of doom. Not following every routine exactly causes people to think that the whole day will fail.
Everyone is different when it comes to anxiety triggers. Compulsions are learned behaviors due to genetics, environment, and social factors. You may have grown up with strict cleaning rules, which creates triggers associated with germs, contaminated food, and sickness.
So, if you didn’t clean fruit properly beforehand, it might encourage an attack. It’s all down to personal obsessions and how people develop them over time. This is why people try anti-anxiety pills or other commonly prescribed drugs when preventing bad OCD episodes.
What Does an OCD Attack Feel Like?
An obsessive-compulsive disorder attack usually feels like a panic attack. Some of these symptoms might be disorientation, nausea, dry mouth, excessive sweating, and harsh breaths. It can feel like an impending sense of doom or fear that won’t go away.
These attacks aren’t usually dangerous, but they can feel scary when you’re going through one. People usually notice anxiety signs like a pounding heart rate. Of course, when your heart is racing fast, you’re bound to get stressed over possible long-term health complications.
Sometimes, you might space out completely and ignore your surroundings. This is because you’re still trying to make sense of what’s wrong. Since the body and mind are connected, it’s common to feel disorientated, like you can’t focus on one single thing.
A Word From a Psychologist
People with obsessive-compulsive disorder can have trouble processing their intrusive thoughts. Sometimes, these thoughts turn into unexpected episodes of panic. Not receiving proper treatment could seriously damage emotional, physical, and mental health.
A clinical psychologist will offer the right medication, but you should use this chance to explore other calming techniques. Small changes in your daily life, like going for a long-distance run or trying meditative exercises, can make a huge difference in your thinking.
You can always consult with your doctor or a licensed therapist about reducing intrusive thoughts. Response prevention can really change your mindset, even though it’s very challenging. Just remember that medical professionals are there to support your progress.
Conclusion
So, how can you stop those dreaded OCD attacks?
Calming obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors could stop your body from going into overdrive. This won’t be a straightforward task, as you’ll need to find the best relaxation techniques. Just take your time when building a routine that improves your mental health.

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: