Understanding the GKI Chart: An Introduction to Glucose Ketone Index
Find out what the GKI is and how you can use it to achieve better results on the keto diet.

Anyone following the ketogenic diet knows how important it is to control blood glucose levels and increase blood ketones to achieve and maintain ketosis for weight loss and optimal health.
You can judge the balance between glucose and ketone levels in your blood by looking for physical signs that your body is burning fat for energy. However, it’s more accurate to measure the levels of glucose and ketones in your blood.
The glucose ketone index (GKI) brings both numbers together, offering a convenient way for you to measure and track your progress on a low-carb, high-fat ketogenic diet.
Continue reading to learn more about the GKI, how to calculate it, and how you can use it to monitor ketosis in your body effectively.
GKI Chart: Monitor Your Progress on Keto
The glucose ketone index (GKI) chart helps make sense of GKI values. Using glucose and ketone values to calculate the glucose ketone index ratio, the chart gives you an indication of the depth of ketosis you are in.
Deep ketosis is achieved with a GKI of 1–3. It can only be attained under medical supervision with strict control of blood glucose and ketone levels. Such metabolic therapy is used for the treatment of epilepsy and other neurological disorders.
A GKI between 3 and 6 indicates moderate ketosis, which is the goal for people with type 2 diabetes and severe obesity. At this level of ketosis, control of blood glucose levels is improved, and insulin resistance is reduced.
For optimal health and weight loss on a ketogenic diet, you are striving for moderate ketosis or a GKI between 6 and 9. At this stage of ketosis, your blood ketone levels typically fall between 0.5 and 3mg/dL, and your glucose reading falls within the normal blood sugar range of 70–125mg/dL (3.9–6.9mmol/L).
What Is the Glucose Ketone Index (GKI)?
The glucose ketone index (GKI) measures the ratio of blood glucose and blood ketone levels to determine the level of ketosis you are in, indicating whether you are in nutritional ketosis or therapeutic ketosis.
The GKI is an indicator of metabolic health. It gives you a snapshot of what your body is using for fuel at any given time based on your glucose and ketone levels, which are measured using a blood glucose and ketone meter.
The biomarker was originally developed as a tool for tracking therapeutic ketosis for the metabolic management of brain cancer. However, nutritional ketosis is helpful for diabetes management, the reduction of insulin resistance, and for those following the ketogenic diet for weight loss.
How to Calculate GKI
Since the glucose ketone index is the ratio of blood glucose levels to blood ketones, you need to know these values to calculate it.
Testing glucose and ketones levels is simple. However, you must have both a glucose meter and a ketone meter, or one that is capable of measuring both glucose and ketone levels, to obtain these values.
To test glucose and ketone values, you simply prick your finger with a clean lancet, place a drop of blood on the glucose and ketone test strips, insert them into the meters, and wait a few seconds to get your glucose and ketone readings.
Finally, you can insert the numbers into a glucose ketone index calculator, which automatically calculates your GKI. Some meters have a built-in GKI calculator and will automatically calculate the value for you.
GKI formula
If you don’t have access to a glucose ketone index calculator, it is easy to calculate the glucose ketone index with the formula below.
Note: If you measure your blood glucose levels in mmol/L, you don’t have to divide the reading by 18.
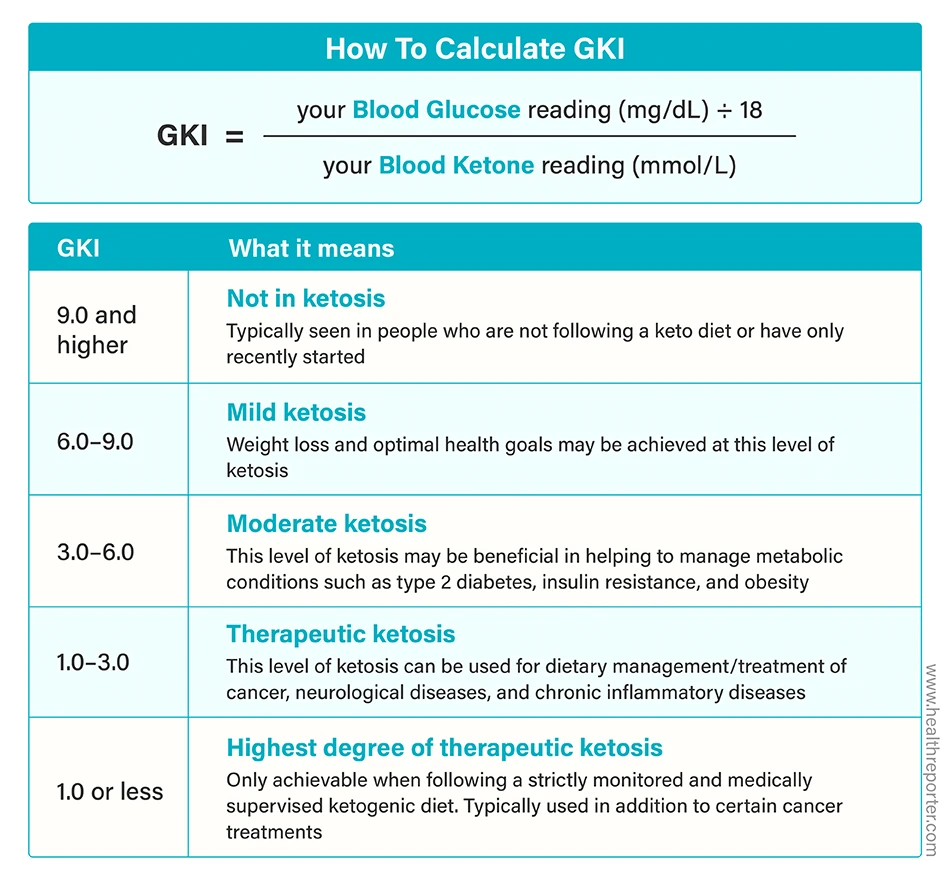
What Is a Good GKI Level?
A good glucose ketone index level depends on whether you are striving for therapeutic ketosis for the management of conditions such as malignant brain cancer or epilepsy or if you are trying to attain nutritional ketosis for weight loss and maintaining optimal health.
All GKI index values less than 9 indicate that your body is burning fat for energy in the form of ketones. However, different levels, ranging from mild to deep ketosis, are beneficial for distinct metabolic health applications.
Readings above 9 are seen in people eating a diet high in carbs, and it indicates that you are not in ketosis.
Optimal GKI for weight loss
The primary purpose of the glucose ketone index is to track the metabolic management of brain cancer patients. Unfortunately, there is insufficient evidence to state the ideal GKI for losing weight.
However, it has been established that nutritional ketosis is indicated by a GKI value between 3 and 9, and values of 6–9 may be effective for weight loss.
Why Is GKI Important?
Knowing and keeping track of your glucose ketone index has numerous benefits, including:
- Weight loss: The GKI can help you achieve and maintain ketosis when you are following the keto diet by showing you which foods spike your blood sugar levels rather than relying on physical signs of ketosis.
- Fasting: Ketone bodies are used for energy when you are fasting. Therefore, the GKI can be used to monitor fasts.
- Insulin resistance: A GKI between 3 and 6 has been shown to be beneficial for reducing insulin resistance.
- Neurological diseases: Ketogenic diets that result in a GKI between 1 and 3 are used for the management of neurological diseases such as epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
- Cancer: Therapeutic ketosis ensures that blood glucose levels are as low as possible to starve cancer cells that are incapable of using ketones for energy. Therefore, the GKI can be applied in conjunction with other cancer treatments.
- Longevity: Although there are no human studies to confirm that calorie restriction resulting in ketosis increases longevity, there are numerous studies in mice that suggest that it does.
- Overall wellness: Following a ketogenic diet improves metabolic health, which improves overall wellness. Therefore, ketosis can help reduce the risk of developing chronic inflammatory diseases, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, depression, and anxiety.
A Word From an MD
The glucose ketone index (GKI) is a valuable biomarker providing insight into a patient’s metabolic health. The ratio of the blood glucose level to the blood ketone level tells us whether the body is using glucose or ketones for energy.
The lower the GKI, the higher the level of ketosis. A very low GKI is required for the metabolic management of conditions such as cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic disorders, while a moderate GKI is useful in the management of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and morbid obesity.
When the GKI is used in clinical practice, it can help guide treatment decisions, including advice for changes in dietary intake and adjustments in medication.
FAQs
Although there is little evidence to suggest it, it is generally accepted that a good GKI level for weight loss is between 6 and 9. It indicates that you are in nutritional ketosis and your dietary intake is maintaining optimum ketone and glucose levels.
The best time to test your GKI is to test it twice a day, 2–3 hours after a meal, so that you can determine how your dietary intake is affecting your blood glucose levels and blood ketone levels.
Although a lower GKI indicates higher ketone levels and lower blood glucose levels, the optimal GKI for weight loss is between 6 and 9. However, improved blood glucose control and improved insulin sensitivity occur at lower levels, which can also aid in weight loss.
Conclusion
The glucose ketone index can help you get the most out of your keto diet by giving you insight into your level of ketosis based on your blood sugar and ketone levels.
Not only is it beneficial for weight loss, but the GKI is an indicator of your metabolic health, and it is used in the metabolic management of brain conditions, cancer, and other metabolic disorders.

















































 Select your language:
Select your language: 










